6.1. Algorithms#
An algorithm is a set of precise instructions that when carried out will solve a task. Any time you are solving a problem you are usually applying some approach, which could be written up as an algorithm. There are many different types of algorithms that can be applied to many different types of problems. The effectiveness of the algorithm can often be measured by how efficient the algorithm (how quickly it reaches a solution) and the quality of the solution it yields.
Key features of algorithms include sequence, selection and iteration.
6.1.1. Sequence#

Instructions that are carried out one after the other are sequential. This means the instructions are carried out in the exact order they are written.
6.1.2. Selection#

Some algorithms can select different pathways to take. In this case the algorithm will check a condition (or sometimes multiple condition) and the evaluation of the condition (i.e. whether the condition is true or false) will control which pathway is taken.
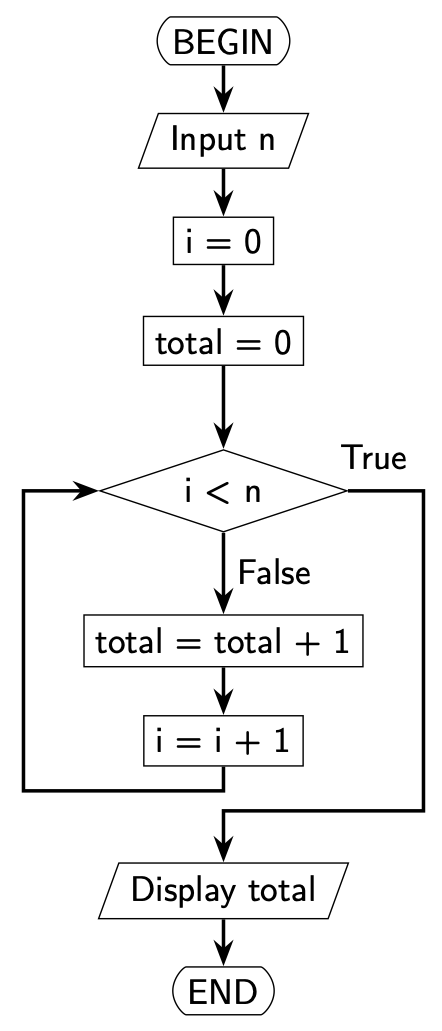
6.1.3. Iteration#
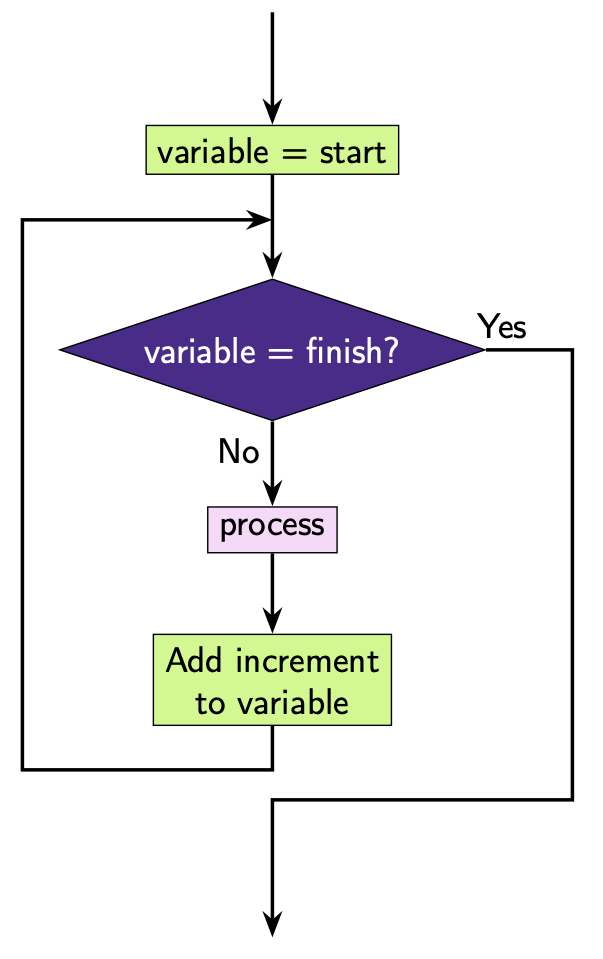
Iteration allows sections of an algorithm to be repeated a fixed number of times or until a certain condition has been met.
6.1.4. Subroutines#
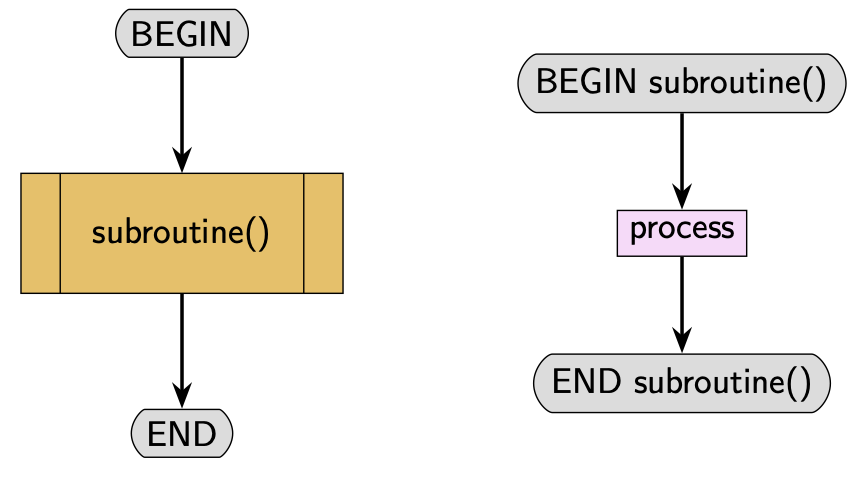
Subroutines are algorithms that can be used in the main algorithm. They can be very useful particularly when there are aspects of the algorithm that are repetitive. They can also make it easier to write algorithms as they can be used to solve subtasks. Use of subroutines often help to make the overall algorithm easier to understand as the main algorithm can be written more concisely.
Question 1
Which of the following could be used to perform iteration? Select all that apply.
ifstatementsif-elif-elsestatementsprintstatementsthe
timemodulewhileloopsforloopsdefining a function
Solution
E. F.
Question 2
Which of the following could be used to perform selection? Select all that apply.
ifstatementsif-elif-elsestatementsprintstatementsthe
timemodulewhileloopsforloopsdefining a function
Solution
Solution is locked
Question 3
Which of the following could be used to perform subroutine? Select all that apply.
ifstatementsif-elif-elsestatementsprintstatementsthe
timemodulewhileloopsforloopsdefining a function
Solution
Solution is locked
Question 4
Question 5
Consider the following flowchart. Which of the following are used in this algorithm? Select all that apply.
Get x
Get y
Get operation
IF operation == 'add' THEN
Display x + y
ELSEIF operation == 'subtract' THEN
Display x - y
ENDIF
Sequence
Selection
Iteration
Subroutine
Solution
Solution is locked
Question 6
Consider the following flowchart. Which of the following are used in this algorithm? Select all that apply.
BEGIN
FOR i = 0 TO 2 STEP 1
doubled = add(i. i)
Display doubled
NEXT i
END
BEGIN add (x, y)
RETURN x + y
END add (x, y)
Sequence
Selection
Iteration
Subroutine
Solution
Solution is locked