5.11. More Joins#
The type of JOIN that we have just learnt is an INNER JOIN There are a few
more types of JOINs that we will cover briefly.
To demonstrate how these joins work, we will continue to use our student
and marks tables.
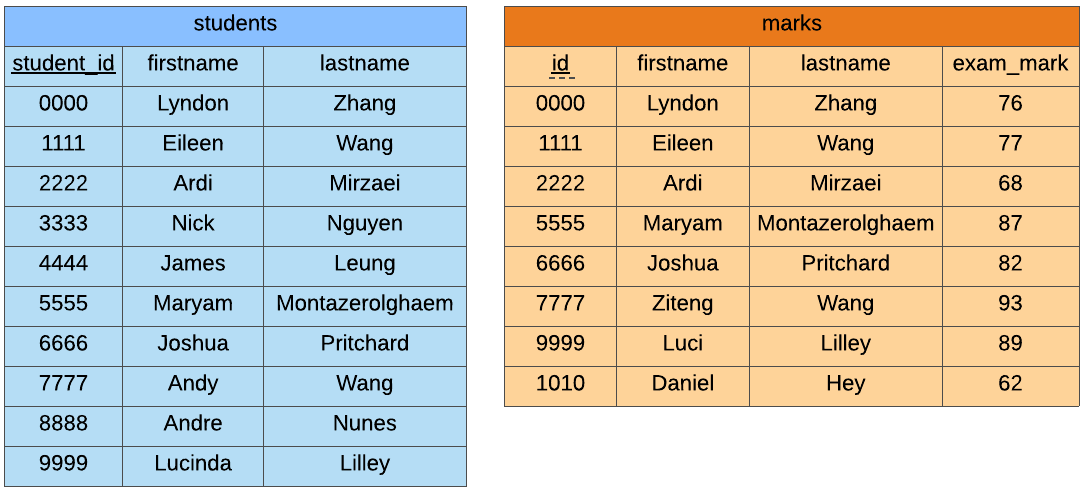
5.11.1. Left Join#
The LEFT JOIN keeps everything from the first table (students) and if there
is a match in the second table (marks), it adds the information from the second
table to the end of first table.
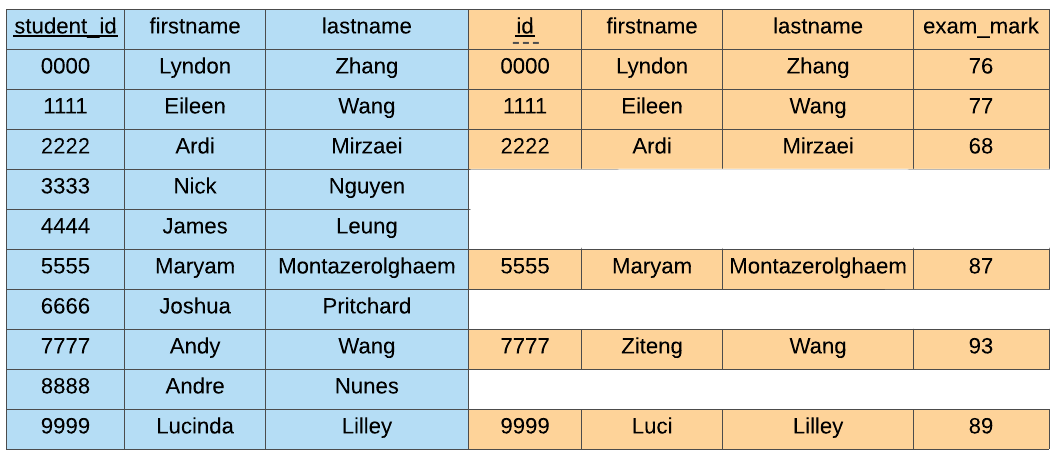
SELECT *
FROM students s
LEFT JOIN marks m
ON s.student_id = m.id;
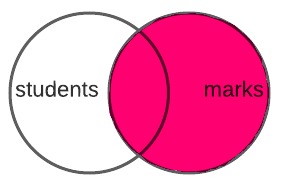
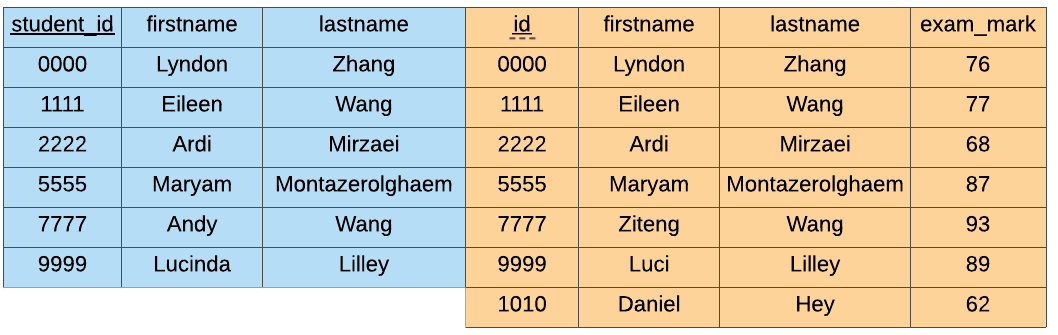
5.11.2. Right Join#
The RIGHT JOIN keeps everything from the second table (marks) and if there
is a match in the first table (students), it adds the information from the
first table to the start of the second table.
SELECT *
FROM students s
RIGHT JOIN marks m
ON s.student_id = m.id;
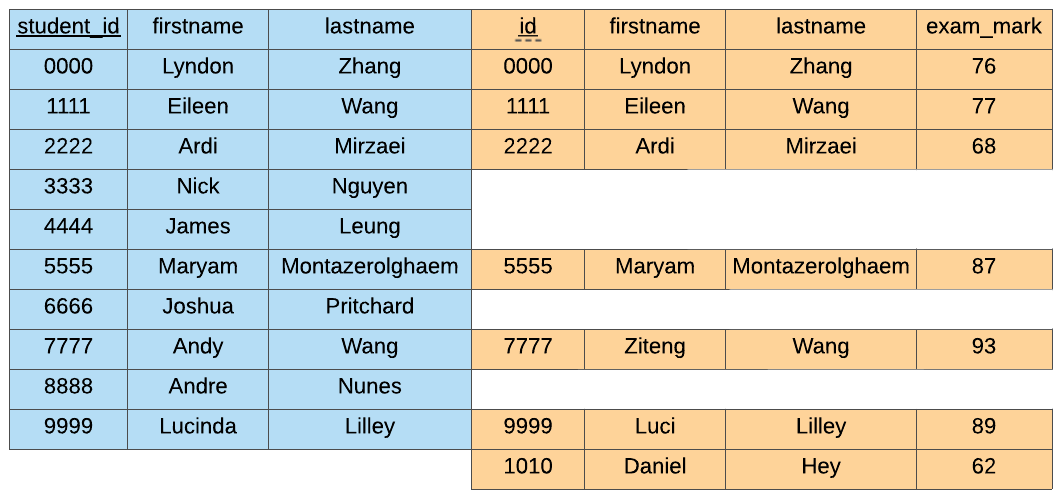
5.11.3. Full Outer Join#
The FULL OUTER JOIN keeps everything!
SELECT *
FROM students s
FULL OUTER JOIN marks m
ON s.student_id = m.id;